




w e d e v e l o p s o l u t i o n s f o r a h e a l t h y f u t u r e
innovations for a healthy future




c o m e a n d v i s i t u s

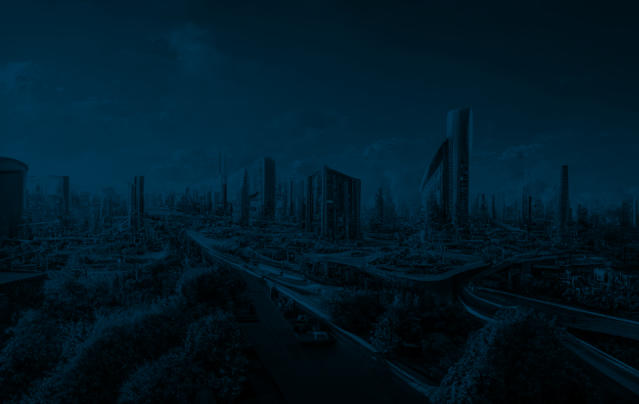
The project

The
project
enables
a
better
future
by
revolutionizing
urban
life
through
innovation
and
sustainability.
Comfort
of
life
is
enhanced
with
connected
homes,
efficient
public
services,
and
effective
municipal
management.
Resources
and
consumption
are
geared
towards
sustainability,
with
the
use
of
renewable
energy,
recycling
systems,
and
energy
recovery
ensuring
greater
efficiency.
Finally,
mobility
becomes
more
eco-friendly
with
traffic
systems,
connected
vehicles,
and
real-time
navigation,
reducing
congestion
and
respecting
the
environment. These advancements transform cities into
sustainable and efficient hubs where quality of life thrives,
shaping a brighter future.
OUR PROJECTS
beCity
s o c i a l a n d c o r p o r a t e e f f o r t
Environmental
policy
must
aim
for
sustainability,
resilience
and
reduction
of
the
ecological
footprint.
It
is
based
on
the
use
of
renewable
energies,
management
of
natural
resources
and
the
circular
economy.
Green
spaces
are
a
priority
with
green
roofs
and
ecological
corridors
in
urban
areas.
Our
social
effort
involves
raising
awareness
of
the
ecological
transition,
with
community
projects
and
environmental
education.
At
the
corporate
level,
it
is
essential
to
maintain
transparency
on
our
impact,
set
ambitious
goals
and
collaborate
with
partners
committed
to
sustainable
development.
By
balancing
innovation
and
responsibility,
our
company
is
a
key
player
in
urban
improvement
and
environmentally friendly solutions.

Copyright © 2024 PWG Europe SL. All rights reserved.
English - United Kingdom

beCity




Public
services
must
be
connected,
efficient
and
accessible
to
all.
Improve
management,
reduce
delays
and
simplify
administrative
procedures
with
digital
platforms.
Eco-responsible
infrastructures
and
optimized
management
of
services
must
also
be
inclusive,
taking
into
account
the
specific
needs
of
citizens.
Collaborative
tools
and
online
dialogue
spaces
must
be present.
Health
services
must
be
innovative,
accessible
and
patient-centric.
They
integrate
advanced
technologies
such
as
telemedicine,
artificial
intelligence
for
early
diagnosis
and
shared
electronic medical records.
These
services
must
ensure
timely
care
through
online
booking
platforms
and
smart triage systems in hospitals.
A
home
should
embody
innovation,
sustainability
and
comfort,
while
integrating
into
the
urban
environment.
Equipped
with
smart
technologies,
such
as
IoT
sensors,
to
optimize
energy,
water
and
security.
They
are
designed
to
be
energy
efficient,
using
sustainable
materials
and
renewable
energy
systems.
Connectivity
ensures
automation
of
devices
and
centralized
management via applications.
The
emphasis
is
also
on
well-being,
with
bright,
well-ventilated
and
healthy
spaces
thanks
to
air
purification
systems.
Finally,
a
house
in
a
smart
city
must
promote
inclusiveness
and
social
interaction,
by
offering
shared
common
spaces
and
access
adapted
to
all.
It
thus
combines
comfort,
modernity,
ecological
and
social
responsibility,
as
well as quality of life.
The
focus
is
on
prevention,
with
personalized
awareness
campaigns
and
connected
health
sensors
to
monitor
patients
remotely.
Infrastructure
must
be
eco-responsible,
well-equipped
and
easily
accessible
to
all,
including
via
smart
public
transport.
In
short,
these
services
combine
efficiency,
innovation
and
humanity
to
meet
needs
in
a
connected
urban
setting.
the public services
the health services
the homes



the water
the energy
the agriculture

beTown



heat exchanger
the vehicules
the networks
the engines
the technologies
heater
reservoir
turbo-alternator
Water
management
must
be
sustainable
and
focused
on
efficiency.
It
relies
on
sensors
monitoring
water
quality
and
levels,
eliminating
waste
and
leaks.
Collection
and
reuse
systems
preserve
natural
resources.
Equitable
management
guarantees
access
for
all
with
responsible
consumption.
Solutions
ensure
sustainability
and
resilient
infrastructure
in
the
face
of
climate
change.
Homes
and
businesses
need
to
be
equipped
with
systems
to
monitor
and
optimize.
Energy
storage
is
essential
to
ensure
stable
power
supply.
Infrastructure
should
include
charging
stations
for
sustainable
mobility
vehicles.
Raising
awareness
of
responsible
consumption
habits
is
key
to
maximizing
energy
efficiency
and
sustaining resources.
Energy
must
be
clean,
sustainable
and
optimized.
Renewable
sources,
such
as
solar,
wind
and
geothermal,
must
be
used
to
reduce
the
carbon
footprint.
Smart
grids
play
a
central
role
by
balancing
production
and
consumption
in
real
time,
while
integrating
distributed
energy
from
buildings
and
infrastructure.
Agriculture
must
be
innovative,
sustainable
and
integrated
into
urban
spaces.
Vertical
farms
and
rooftop
gardens
help
to
optimise
space
by
providing
fresh
food
nearby.
The
use
of
IoT
sensors,
drones
and
artificial
intelligence
can
monitor
crops,
save
water
and
improve
yields.
Urban
agriculture
must
also
be
environmentally
friendly,
with
practices
such as hydroponics and aquaponics
consuming
fewer
natural
resources.
Organic
waste
can
be
composted
to
enrich
the
soil.
These
initiatives
bring
citizens
closer
to
food
production,
promoting
greater
ecological
awareness
and
healthier
eating.
Agriculture
is
therefore
at
the
crossroads
of
innovation,
sustainability
and community well-being.
Networks
and
infrastructure
must
be
sustainable
and
interconnected.
Roads
integrate
sensors
to
monitor
traffic,
infrastructure
and
weather
conditions.
Materials
used
for
roads
and
buildings
are
capable
of
self-healing,
extending
their
lifespan
and
minimizing
maintenance.
Infrastructure
is
designed
to
promote
soft
modes
of
transport,
safe
cycle
paths
and
wide
sidewalks for pedestrians.
Parking
lots
reduce
congestion
by
guiding
drivers
to
available
spaces.
Underground
networks
are
modernized
to
support
the
growing
needs
for
connectivity
and
electrical
charging.
Public
spaces,
bridges
and
tunnels,
are
designed
to
withstand
natural
disasters
and
integrate
technologies
promoting
lighting
and
intelligent energy management.
Transportation
must
be
connected,
sustainable
and
accessible
to
all.
Electric,
compressed
air
or
clean
energy
vehicles
dominate,
powered
by
renewable
energy,
to
eliminate
carbon
emissions.
Public
and
autonomous
transport
are
integrated
into
networks
that
allow
efficient
traffic
management
and
route
optimization.
Engine
technologies
are
evolving
towards
zero-
emission systems, such as electric,
hydrogen,
compressed
air
or
synthetic
fuel
engines.
Charging
infrastructures
of
all
types
are
deployed
on
a
large
scale.
Shared
mobility,
bicycles
and
scooters,
encourage
collaborative
modes
of
transport
that
reduce
congestion.
Digital
tools
centralize
options
offering
seamless
and
personalized
journeys.
Transportation
is becoming a pillar of quality of life.
About
Learn more
Housing project
Villages project
Smart cities project
Link to download - forms
Office :
PWG Europe SL
office and factory
Alicante - Spain
For
any
inquiry,
please
contact
us,
we
will
reply shorthly :
contact@pwge.info



3
2
1


Comfort &
well-being
a 'smart' city has as its primary
objective to ensure the comfort
and well-being of its citizens

a 'smart' city has as a second objective
to have an optimal management of
needs, resources and waste
Consumption
& resources


a 'smart' city has as its third objective to
manage infrastructures, navigation, networks
and connected ways of transportation
Transport &
travelling





































![Fermer [x]](index_htm_files/close.png)



